ctrl+U-> Make lower case
shift+ctrl+U->make upper case
ctrl+k+U->Uncomment
ctrl+k+C->Comment
shift+ctrl+U->make upper case
ctrl+k+U->Uncomment
ctrl+k+C->Comment
<script type="text/javascript"> var ck_name = /^[A-Za-z0-9 ]{3,20}$/; var ck_email = /^([\w-]+(?:\.[\w-]+)*)@((?:[\w-]+\.)*\w[\w-] {0,66})\.([a-z]{2,6}(?:\.[a-z]{2})?)$/i var ck_username = /^[A-Za-z0-9_]{1,20}$/; var ck_password = /^[A-Za-z0-9!@#$%^&*()_]{6,20}$/; function validate(form){ var name = form.name.value; var email = form.email.value; var username = form.username.value; var password = form.password.value; var gender = form.gender.value; var errors = []; if (!ck_name.test(name)) { errors[errors.length] = "You valid Name ."; } if (!ck_email.test(email)) { errors[errors.length] = "You must enter a valid email address."; } if (!ck_username.test(username)) { errors[errors.length] = "You valid UserName no special
char ."; } if (!ck_password.test(password)) { errors[errors.length] = "You must enter a valid Password "; } if (gender==0) { errors[errors.length] = "Select Gender"; } if (errors.length > 0) { reportErrors(errors); return false; } return true; } function reportErrors(errors){ var msg = "Please Enter Valide Data...\n"; for (var i = 0; i<errors.length; i++) { var numError = i + 1; msg += "\n" + numError + ". " + errors[i]; } alert(msg); } </script>
<html> <head> <title>Url validation using regex</title> <script type="text/javascript"> function validate() { var url = document.getElementById("url").value; var pattern = /(ftp|http|https):\/\/(\w+:{0,1}\w*@)?(\S+)(:[0-9]+)?(\/|\/([\w#!:.?+=&%@!\-\/]))?/; if (pattern.test(url)) { alert("Url is valid"); return true; } alert("Url is not valid!"); return false; } </script> </head> <body> <h2>Validating Url..</h2> Url :<input type="text" name="url" id="url" /> <input type="submit" value="Check" onclick="validate();" /> </body> </html>
using System.ComponentModel; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations; namespace MvcApplication1.Models { public class Product { public int Id { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(10)] public string Name { get; set; } [Required] public string Description { get; set; } [DisplayName("Price")] [Required] [RegularExpression(@"^\$?\d+(\.(\d{2}))?$")] public decimal UnitPrice { get; set; } } }
DataAnnotations library to specify and verify validation rules for domain entities.Customer in system by holding Customer related information. I assume when adding a new customer into the system, you must provide CustomerID and CompanyName, and the CompanyName must have maximum 10 characters. If you provided value for Country, then the value must be USA. If you provided value for Phone, then the phone number must have correct format. In summary, the Customer entity has following validation rules:CustomerID is requiredCompanyName is requiredCompanyName can have maximum 10 charactersCountry can only be USA when there is a valuePhone must have format ###-###-#### (# means digit) when there is a valueDataAnnotations is a library in .NET Framework. It resides in assembly System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations. The purpose of DataAnnotations is to custom domain entity class with attributes. Therefore, DataAnnotations contains
validation attributes to enforce validation rules, display attributes
to specify how data from the class or member is displayed, and data
modeling attributes to specify the intended use of data members and the
relationships between data classes. One example of validation attribute
is RequiredAttribute that is used to specify that a value must be provided. One example of display attribute is DisplayAttribute that is used to specify localizable strings for data types and members that are used in the user interface. And, one example of data modeling attribute is KeyAttribute that
is used to specify the property as unique identity for the entity. We
will only show how to use validation attributes in here to verify
validation rules for domain entity. Customer entity, we need to put two built-in validation attributes of DataAnnotations, RequiredAttribute and StringLengthAttribute, on Customer class. The Customer class will be something like this:RequiredAttribute and StringLengthAttribute in detail: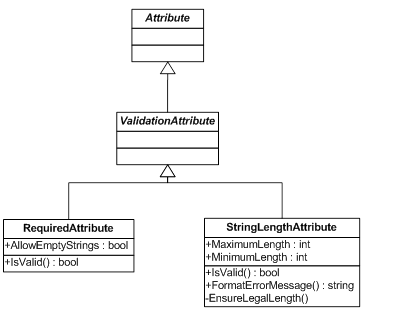
RequiredAttribute and StringLengthAttribute all inherit from ValidationAttribute that is the base class of all validation attributes.RequiredAttribute and StringLengthAttribute, we are only able to specify validation rules for the first three requirements, how about the last two requirements: Country can only be USA when there is a value and Phone must
have format ###-###-#### (# means digit) when there is a value. The
solution is to create custom validation attributes for them. We need to
create two custom validation attributes here, one is for Country and another one is for Phone. 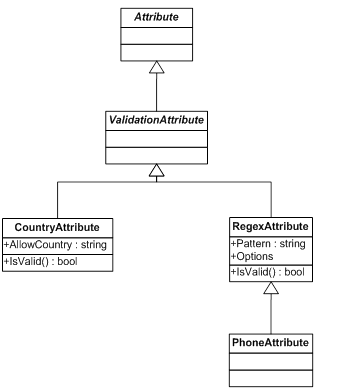 At the end,
At the end, Customer class with all validation attributes on it will be like this:Customer entity, we can verify Customer against the rules in our application with DataAnnotations.Validator class.ValidationHelper is a helper class that wraps up the call to DataAnnotations.Validator.validateAllProperties, of TryValidateObject method is a Boolean type variable. You must pass in true to
enable verification on all types of validation attributes, include the
custom validation attributes we used above. If you pass in false, only RequiredAttribute used on entity will be verified. The name of this parameter is very misleading. 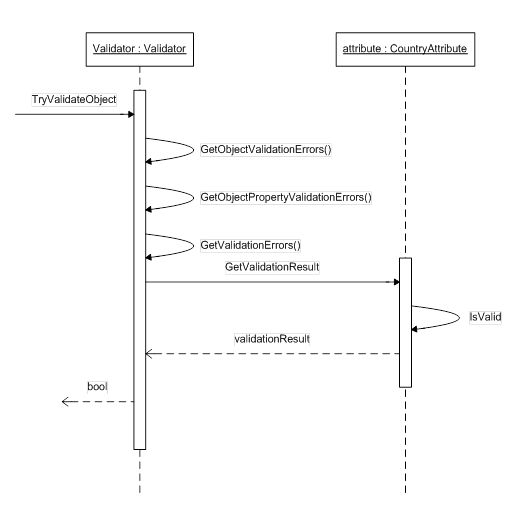
DataAnnotations library provides an easy way to specify
and verify validation rules on domain entity. Also, it is opening for
change by design, so developers can add their own validation attributes
for their own situation. By specifying validation rules on domain entity
directly allow upper layers have no worry of validation anymore.